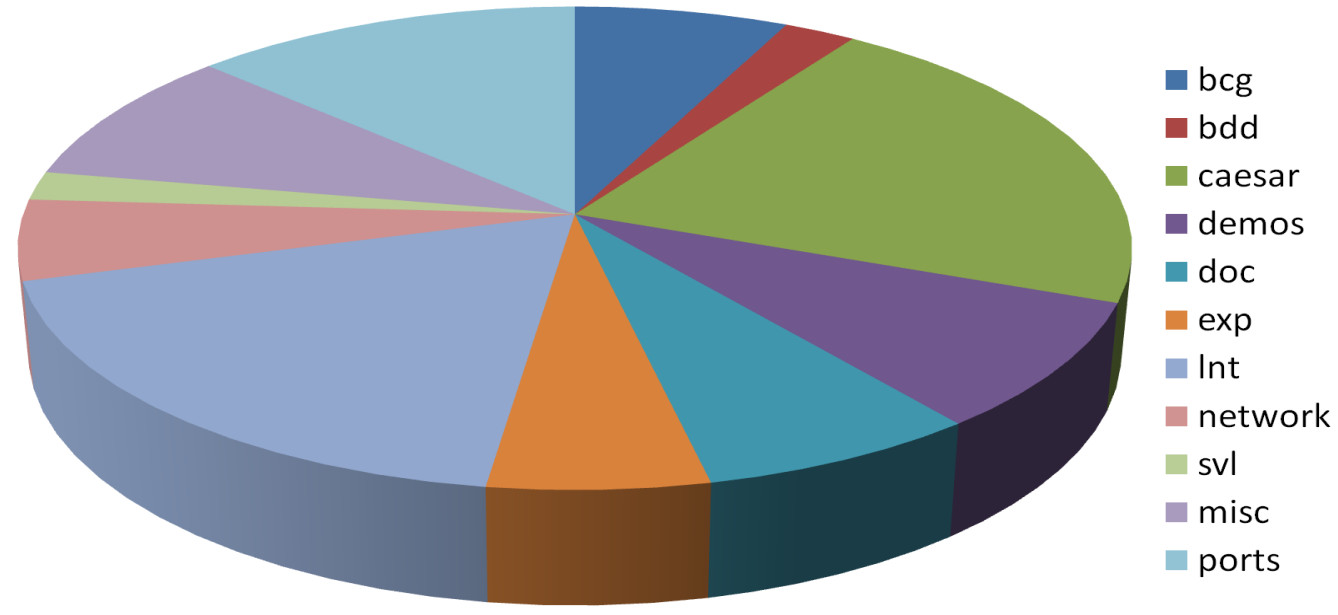
This section summarizes the main enhancements in the various components of
CADP. For more details, please refer to the CADP
- BCG
-
The conventions for string notations to represent "raw" values (i.e., values
whose type is not a predefined one, but a custom type defined by the user)
have improved, together with the associated conversion algorithms for
reading/writing raw values from/to strings. The BCG_WRITE manual page has
been updated to more accurately describe how label fields of type "raw" are
parsed. The behaviour of the functions bcg_character_scan(), bcg_string_scan(),
bcg_real_scan(), and bcg_raw_scan() has been carefully revised, and all
the BCG libraries and tools (especially BCG_IO) have been modified to follow
the new conventions and emit better diagnostics when label fields contain
incorrect notations of raw values. Also, BCG_IO can now convert very long
execution sequences into SEQ or LOTOS files without causing stack overflow.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2208 #2209 #2211 #2214 #2215 #2248 #2265 #2266.
- CAESAR and CAESAR.ADT
-
Following the writing of the new CADP manual page for LOTOS, the front-end
of CAESAR and CAESAR.ADT was carefully inspected, which led to various bug
fixes regarding type signatures, error messages for overloaded functions,
renaming/actualization of sorts and operations, equations for renamed
operations, C-language reserved keywords, implementation of numeral sorts,
and iterators over these sorts. Another bug was fixed for the "-external"
option of CAESAR and a new "-numeral" option was introduced.
Also, the C identifiers automatically generated by CAESAR.ADT for sorts,
operations, tester and selector macros have been simplified. So doing,
the size of the C code generated by CAESAR.ADT was reduced by 4,73%
(measured on 3.2 gigabytes of generated C code). As the new conventions
are not backward compatible, the UPC migration tool was extended to ease
transitioning the existing LOTOS and C files.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2179 #2180 #2190 #2220 #2222 #2223 #2224 #2226 #2229 #2231 #2232
#2233 #2234 #2235 #2236 #2243 #2244.
- CAESAR.BDD
-
The CAESAR.BDD tool that analyzes NUPN (Nested-Unit Petri Nets) models
and serves to prepare the yearly Model Checking
Contest has been enhanced with two new options "-initial-places" and
"-initial-tokens". It now properly handles the case where the initial marking
contains more than 2^31 tokens. The output of the "-mcc" option has been made
more precise when the NUPN under study is conservative or sub-conservative.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2155 #2163 #2164 #2165 #2167.
- DEMOS
-
The demo 12 (Message Authentication Algorithm) and demo 31 (SCSI-2 bus
arbitration protocol) have been manually translated from LOTOS to LNT.
Additionally, demo 12 has been deeply revised by simplifying its LOTOS, LNT,
and C code, by taking advantage of the imperative-programming features of LNT,
and by enriching the LNT specification with the test cases contained in the
original MAA description. This allowed to detect and correct a mistake in the
C code implementing function HIGH_MUL(). Other CADP demos (namely demos
05, 16, 19, and 36) have also been simplified and/or enhanced in various ways.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2158 #2160 #2161 #2162 #2176 #2193 #2263 #2272 #2273 #2274.
- DOC
-
Sustained effort was made to improve the documentation of the CADP toolbox.
Various corrections have been brought to the CADP manual pages. A 27-page
manual page explaining how the LOTOS language is implemented has been
written, and the manual pages of the CAESAR and CAESAR.ADT compilers have
been also updated. To make documentation more readable, the EVALUATOR3,
and EVALUATOR4 manual pages have been splitted each in two pages, so as to
better distinguish between the languages (namely, MCL3 and MCL) and their
associated model checkers. The CADP distribution has been made leaner by
keeping only the essential papers, and the "publications" and "tutorial"
pages of the CADP web site have been enriched and reorganized.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2157 #2171 #2175 #2177 #2178 #2181 #2182 #2183 #2191 #2192 #2202
#2219 #2252.
- EXP
-
The parallel composition operator "par" of the EXP language has been extended
in several ways. From now on, local synchronization interfaces have the
same syntax as global synchronization interfaces and accept synchronization
degrees of the form #N. Also, synchronization degrees #0 and #1 have been
added to, respectively, prevent a given gate from being fired or explicitly
indicate that a given gate is not synchronised. A bug in EXP.OPEN has been
fixed and better messages are now emitted to warn about dubious usage of
the "par" operator.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2169 #2203 #2204 #2205 #2212.
- LNT
-
In 2016, the long-term effort to enhance the LNT language and its tools
has been pursued. LNT has been enriched with a new statement "use X" that
suppresses compiler warnings when a variable X is assigned but not used.
The syntax of LNT expressions has been modified so that field selections
("E.X"), field updates ("E1.{X = E2}"), and array accesses ("E1 [E2]") can
now be freely combined without extra parentheses. LNT programs can now
import predefined libraries, and two such libraries (BIT.lnt and OCTET.lnt)
have been introduced.
A move towards "safer" LNT exceptions has started. The syntax for exceptions
in function declarations has been modified and the semantics of LNT has
shifted from "unchecked" to "checked" exceptions: exception parameters,
if any, must be explicitly mentioned when a function is called. Such
exception parameters can now be passed using either the named style or
the positional style.
A few static-semantics constraints have been relaxed; for instance, it is
no longer required that actual gate parameters be different when calling a
process. Various bugs have been fixed. Several error/warning messages have
been made more precise, and the format of LNT error/warning messages has
been aligned on that of GCC. Finally, the LNT2LOTOS Reference Manual has
been updated and enhanced.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2154 #2156 #2159 #2166 #2170 #2173 #2194 #2201 #2217 #2218 #2225
#2228 #2230 #2230 #2241 #2242 #2245 #2251 #2269 #2270 #2271 #2275.
- NETWORK
-
The code of the "caesar_network_1" library, which is a building block
for the distributed verification tools of CADP, has been carefully
scrutinized and split into five logically-independent modules. Nine problems
have been detected and solved, among which a flaw in the distributed
termination algorithm: the entire network could freeze if a worker process
crashed too early, before the opening of TCP sockets. From now on, a better
distributed termination algorithm is used, which supports the coexistence
of several networks, ensures that all connections are closed before
terminating, and produces more informative traces indicating which worker
has triggered termination. Also, the improved "caesar_network_1" library
checks that all workers operate in directories that are pairwise distinct,
mutually disjoint, and different from the working directory of the
coordinator process.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2195 #2216 #2258 #2259 #2260 #2264 #2268.
- SVL
-
The SVL language has been extended to include the generalized parallel
composition operator with synchronization degrees in synchronization
interfaces that has been recently introduced in EXP.OPEN. Two bugs have
also been corrected.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2168 #2213 #2255.
- MISC
-
Enhancements and bug fixes have been brought to other CADP components,
including CADP_MEMORY, EUCALYPTUS, INSTALLATOR, OCIS, RFL, TST, and XTL.
The style files for the various editors supported by CADP have been
updated to take into account the recent features added to LNT. The
predefined MCL libraries of the EVALUATOR model checker have been
modified to generate more explanatory diagnostics for the inevitability
operators.
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2184 #2187 #2188 #2207 #2221 #2227 #2237 #2238 #2240 #2246 #2247
#2249 #2250 #2262 #2267.
- PORTS
-
Although CADP is mostly used on Linux, specific effort has been made to
target other execution platforms. Concerning macOS: CADP now supports
the recent versions 10.10 ("Yosemite"), 10.11 ("El Capitan"), and 10.12
("Sierra"). Concerning Windows: changes have been brought to support
Windows 10 and the 64-bit version of Cygwin (previously, only the 32-bit
version was supported). Other adaptations were required to handle the
recent versions of Cygwin packages, MinGW C compiler, and Mintty shell,
as well as the case where Cygwin is not installed in "C:\", but in either
"C:\Cygwin" or "C:\Cygwin64".
For details, see HISTORY entries:
#2172 #2174 #2185 #2186 #2189 #2196 #2197 #2198 #2199 #2200 #2206
#2210 #2253 #2254 #2256 #2257 #2261.
We are extremely grateful to the following scientists, who provided us with
valuable feedback and advice about the use of CADP:
and all other persons we may forget.


 Back to the CADP Home Page
Back to the CADP Home Page